Welcome back to HealthPedia24.com, your trusted portal for evidence-based dermatological insights. After exploring the structural power of Peptides and the protective ecosystem of the Skin Microbiome, it is time to discuss the “bodyguard” of your skincare routine: Ferulic Acid.
In 2026, the focus of skincare has shifted from aggressive correction to Preventative Longevity. We no longer want to just fix damage; we want to stop it before it happens. If Vitamin C is the “King” of brightening, Ferulic Acid is the “General” that protects the King and doubles his power.
In this comprehensive guide, we break down why this plant-based antioxidant is a non-negotiable for anyone living in a high-pollution, high-UV environment.
What Is Ferulic Acid?
Ferulic acid is a phenolic compound, specifically a hydroxycinnamic acid, naturally occurring in the cell walls of plants such as rice bran, oats, apples, oranges, and coffee. Chemically, it’s known as 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid, with a structure that includes a benzene ring, methoxy group, and carboxylic acid, contributing to its antioxidant prowess. In nature, it helps plants resist UV radiation and pathogens, a function that translates to skincare benefits.
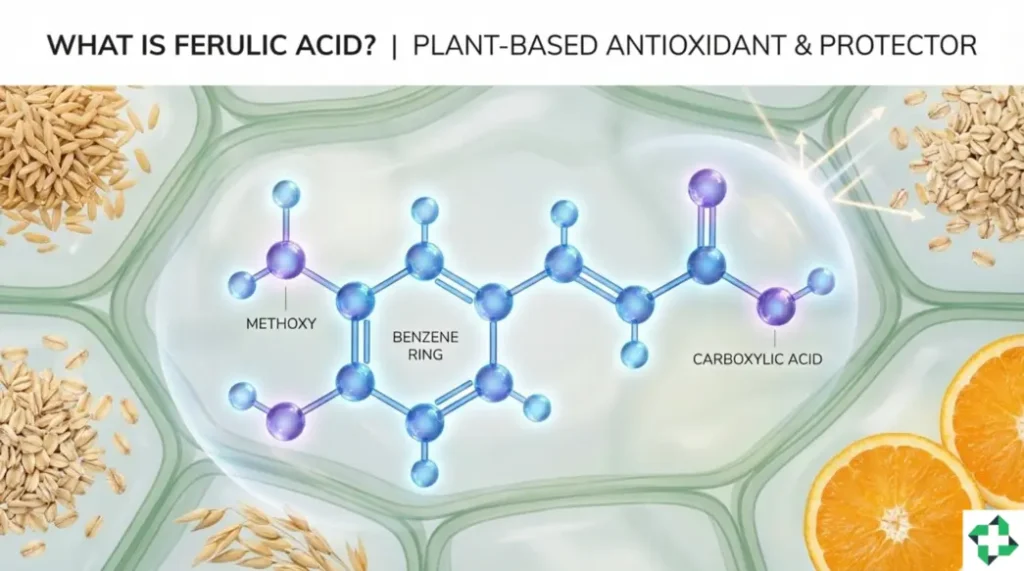
In cosmetic applications, ferulic acid is often extracted or synthesized for stability, appearing as a white or yellowish powder. It’s soluble in ethanol and propylene glycol but less so in water, which influences formulation. Concentrations typically range from 0.5% to 3% in products, ensuring efficacy without irritation. Unlike some acids (e.g., AHAs), it’s not exfoliating but focuses on protection and enhancement.
This compound’s bioavailability improves when combined with delivery systems like liposomes, allowing better penetration into the stratum corneum. Overall, ferulic acid exemplifies how plant-based antioxidants can fortify human skin against daily assaults.
Historical and Traditional Uses
Ferulic acid’s roots trace back to traditional medicine systems where its source plants were valued. In Chinese medicine, rice bran (rich in ferulic acid) was used for digestive health and vitality, indirectly benefiting skin via internal wellness. Ayurvedic practices incorporated ferulic acid-containing herbs like artichoke for liver support, which ties into skin detoxification.
In the 19th century, ferulic acid was isolated from ferula plants, leading to early pharmacological studies. By the 20th century, its antioxidant properties were recognized in food preservation, preventing lipid oxidation. Skincare adoption surged in the 2000s, following patents like Skinceuticals’ C E Ferulic serum in 2005, which popularized its synergy with vitamins.
Today, it’s embraced globally for anti-aging, with ongoing research expanding its applications beyond topical use to supplements for systemic benefits.
Mechanism of Action: How It Works
To understand Ferulic Acid, we must talk about Free Radicals. These are unstable molecules caused by UV rays, cigarette smoke, and city pollution. They act like “molecular scavengers,” stealing electrons from your healthy skin cells, which leads to DNA damage, collagen breakdown, and premature aging.
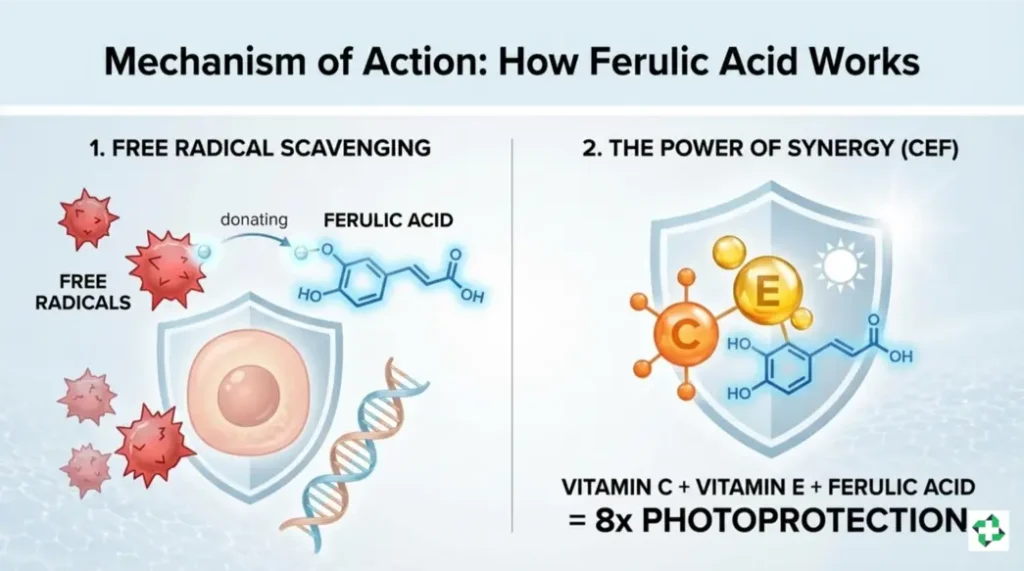
1. Free Radical Scavenging
Ferulic Acid “sacrifices” itself by donating an electron to these free radicals, neutralizing them before they can attack your collagen.
2. The Power of Synergy (CEF)
The most famous thing about Ferulic Acid is not what it does alone, but what it does for other vitamins. On its own, Vitamin C (L-Ascorbic Acid) is notoriously unstable and degrades when exposed to light or air.
- Stabilization: Ferulic Acid stabilizes Vitamin C, preventing it from oxidizing.
- Multiplication: When combined with Vitamin C and Vitamin E, Ferulic Acid increases the photoprotective (sun-protecting) effectiveness of the formula by 8 times.
Vitamin C + Vitamin E + Ferulic Acid = 8 times Photoprotection
Benefits of Ferulic Acid Backed by Science
Evidence supports several benefits:
1. Photo-Aging Prevention
While it is not a sunscreen, Ferulic Acid significantly reduces the damage caused by UV rays that “leak” through your SPF. It helps prevent the formation of “sun spots” and leathery skin texture.
2. Redness and Inflammation Control
Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, it is excellent for calming skin that has been over-exposed to the sun or environmental toxins.
3. Brightening & Hyperpigmentation
By inhibiting Tyrosinase (the enzyme responsible for melanin production), Ferulic Acid helps fade existing dark spots and prevents new ones from forming after a breakout.
4. Preservation of Collagen and Elastin
By neutralizing the enzymes that eat away at your skin’s structure, it helps maintain the “snap-back” quality of young skin.
The 2026 Comparison: Ferulic Acid vs. Others
| Feature | Ferulic Acid | Vitamin C (L-AA) | Resveratrol |
| Main Role | Stabilizer & Protector | Brightener & Builder | Overnight Repair |
| Best Time | Morning (with SPF) | Morning | Evening |
| Stability | High | Low (Oxidizes fast) | Moderate |
| Skin Type | All (even sensitive) | Can be irritating | Very Soothing |
How to Use Ferulic Acid Correctly
To maximize the benefits for your skin, layering is key.
1. The Morning Routine (Recommended)
Because its main job is to fight environmental damage, Ferulic Acid is most effective when applied in the morning.
- Step 1: Cleanse with a gentle, pH-balanced wash.
- Step 2: Apply a Vitamin C + E + Ferulic Acid Serum.
- Step 3: Apply a lightweight moisturizer.
- Step 4: Sunscreen (SPF 50+). This is the most important step; the serum and SPF work together like a shield and armor.
2. Avoiding Conflicts
- Exfoliating Acids: Avoid using Ferulic Acid at the exact same time as strong AHAs/BHAs (like Glycolic Acid). The low pH of acids can sometimes cause irritation when mixed with potent antioxidants.
- Copper Peptides: As we mentioned in our Peptides guide, Copper Peptides and strong antioxidants like Ferulic Acid can cancel each other out. Use one in the morning and one at night.
Also Visit:
How to Double Cleansing : Ultimate Guide [2026]Side Effects and Considerations
Ferulic Acid is generally safe, but there are a few things to watch for:
- The “Hot Dog” Smell: Pure Ferulic Acid combined with Vitamin C often has a metallic or “hot dog water” scent. This is normal and a sign of the chemical reaction, not that the product is bad.
- Oxidation: If your serum turns dark orange or brown, the Ferulic Acid could no longer stabilize the Vitamin C. It’s time to throw it away.
- Sensitivity: Those with extremely sensitive skin or a damaged microbiome (see our Microbiome guide) might feel a slight tingle. Always patch test first.
Conclusion
Ferulic Acid is the “unsung hero” of modern skincare. While it doesn’t get as much hype as Retinol or Hyaluronic Acid, it is the glue that holds a high-performance routine together. By stabilizing your actives and providing a secondary line of defense against the sun, it ensures that your skin remains resilient for years to come.
At HealthPedia24.com, we recommend every adult over the age of 25 incorporate a Ferulic Acid-based serum into their morning routine to safeguard their skin’s future.
Sources : PubMed Central ( What is Ferulic Acid ), Cleveland Clinic ( Benefits of Ferulic Acid ), Healthline ( Side Effects of Ferulic Acid- Sensitivity ).
Disclaimer
The content provided in this article, “Ferulic Acid 2026: Double Your Vitamin C Power for Radient Skin,” by HealthPedia24.com is for general informational and educational purposes only and is NOT a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Skin rashes and chronic redness can be symptoms of various underlying conditions, including infections or autoimmune diseases. Always consult a qualified dermatologist or healthcare professional with any questions regarding a medical condition. If you experience severe swelling or an allergic reaction, seek emergency medical attention immediately. HealthPedia24.com is not responsible for any individual adverse reactions resulting from the use of the information provided herein.
For more Information you can read our Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ferulic acid?
Ferulic Acid is a potent plant-based antioxidant found naturally in the cell walls of grains like rice, oats, and wheat. In skincare, it is a high-performance active used primarily to protect the skin from environmental aging and to keep other ingredients stable.
What is the role of ferulic acid?
Its primary role is as a “Stabilizer and Booster.” While it fights free radicals on its own, its most critical job is preventing Vitamin C and Vitamin E from oxidizing (breaking down). By stabilizing these vitamins, it makes your entire skincare routine significantly more effective.
What does ferulic acid do on the skin?
On the skin, Ferulic Acid acts as a biological shield. It neutralizes free radicals caused by pollution and UV rays, which prevents wrinkles and sagging. It also helps reduce inflammation, calms redness, and works to fade dark spots for a more even skin tone.
Which is better: Niacinamide or Ferulic Acid?
Neither is “better” because they solve different problems. Niacinamide is best for controlling oil, minimizing pores, and repairing the skin barrier. Ferulic Acid is superior for antioxidant protection and anti-aging. For 2026 skincare standards, we recommend using both: Ferulic Acid in the morning and Niacinamide at night.
What foods are high in ferulic acid?
You can boost your internal antioxidant levels by eating foods rich in Ferulic Acid. The highest concentrations are found in whole grains (brown rice, oats, and whole wheat), seeds (flaxseeds), and vegetables like sweet corn, tomatoes, and eggplant.

